Table of Contents
In this article, we will look into 3 easy ways to check/find OpenSUSE Linux version. You can find two important files in OpenSUSE Linux version i.e /etc/os-release and /usr/lib/os-release which contains all the information about the OS. You can simply open the file with cat command and check the release version. Other important tools that you can use is lsb-release and hostnamectl. You will find both of the utilities installed by default in recent OpenSUSE distribution hence you don’t have to install them separately. Both of the tools are explained below in detail.

Easy Ways to Check/Find OpenSUSE Linux Version
Also Read: 6 Easy Steps to Setup and Manage Log rotation Using logrotate in Linux
Method 1: Check/Find OpenSUSE Version from /etc/os-release file
First method that you can use to check the OpenSUSE version is through file /etc/os-release. If you open the file using cat /etc/os-release command then you can get the complete information about OpenSUSE.
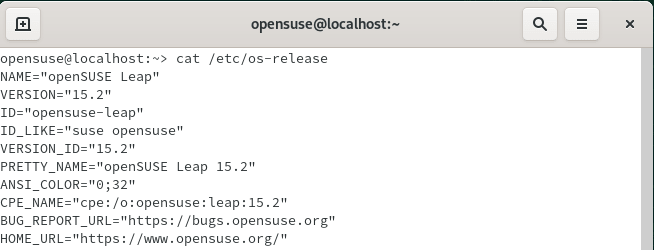
Below important information you can get from /etc/os-release file.
Name : A string which identifies the operating system without version component.
Version : A string identifies the version of the operating system without any os information.
ID : A string identifies the operating system without any version information.
ID_LIKE : It is a list of identifiers which identifies the operating system.
VERSION_ID : A string which identifies the version of the operating system.
PRETTY_NAME : A user friendly OS name.
ANSI_COLOR : User friendly color used to show the OS name.
CPE_NAME : It is a CPE name for OS in URI Binding Syntax.
BUG_REPORT : It shows the Bug Reporting Page URL.
HOME_URL : It shows the home page of the Operating System.
Method 2: Check/Find OpenSUSE Version Using lsb-release Utility
Another important method is through lsb-release command where one can check the OpenSUSE version by using lsb-release -a command as shown below. More can be checked on lsb-release Man Page.
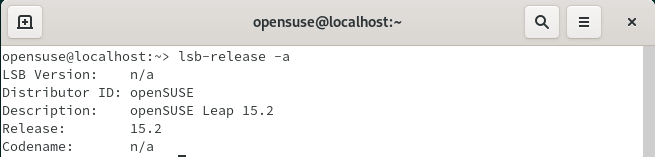
Below are the important information provided by the lsb-release output:-
LSB Version : A string displays the version of lsb-release utility.
Distributor ID : A string displays the ID of distributor.
Description : A string displays the OS distribution name and version.
Release : It displays the release version of OS.
Codename : It displays the codename of the current operating system.
You can also check all the available options of lsb-release using lsb-release -h command as shown below.
localhost:~ # lsb-release -h lsb-release v3.1 prints certain LSB (Linux Standard Base) and Distribution information. Usage: lsb-release [OPTION]... With no OPTION specified defaults to -v. Options: -v, --version Display the version of the LSB specification against which the distribution is compliant. -i, --id Display the string id of the distributor. -d, --description Display the single line text description of the distribution. -r, --release Display the release number of the distribution. -c, --codename Display the codename according to the distribution release. -a, --all Display all of the above information. -s, --short Use short output format for information requested by other options (or version if none). -h, --help Display this message.
Method 3: Check/Find OpenSUSE Version Using hostnamectl utility
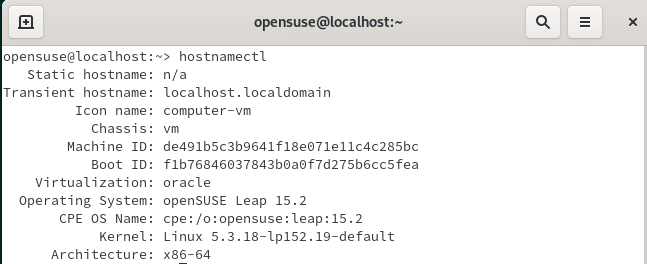
You can also use another useful utility called hostnamectl to check the OpenSUSE Linux version as shown in below figure. Here you can get other important information like Server hostname, Chassis, Machine ID, Kernel version, architecture type etc.
You can also check all the available options of hostnamectl using hostnamectl -h command as shown below.
localhost:~ # hostnamectl -h hostnamectl [OPTIONS...] COMMAND ... Query or change system hostname. -h --help Show this help --version Show package version --no-ask-password Do not prompt for password -H --host=[USER@]HOST Operate on remote host -M --machine=CONTAINER Operate on local container --transient Only set transient hostname --static Only set static hostname --pretty Only set pretty hostname Commands: status Show current hostname settings set-hostname NAME Set system hostname set-icon-name NAME Set icon name for host set-chassis NAME Set chassis type for host set-deployment NAME Set deployment environment for host set-location NAME Set location for host
Popular Recommendations:-
Migrate CentOS 8 to CentOS Stream 8 in 6 Easy Steps
26 iostat, vmstat and mpstat command examples to Monitor Linux Performance
Practical Steps to Install iostat and mpstat command on Linux(RHEL/CentOS 7/8)
16 Fdisk command examples to Manage Disk Partitions in Linux
How to Convert/Change time to epoch time using date utility on Linux/Unix Server
How to Install jq(JSON Processor) on RHEL/CentOS 7/8
7 Simple Steps to Install MTR(My Traceroute) on Linux(RHEL/CentOS 7/8)
Python3: ModuleNotFoundError: No Module Named “prettytable” in Linux
